10 Adding Additional Packages in R/Python
Adding Additional Packages in R/Python
The ADRF has an internal package repository, so users can install packages for R and Python themselves.
The repositories that are currently mirrored in the ADRF are CRAN for R packages and PyPi.org for Python. There is currently no access to packages hosted on Github or other mirrors.
If you are working in a shared workspace for a project, each user in the project must install the packages, there is no shared package installation for projects.
R packages
To install R packages, simply type:
install.packages("packagename")

and the package will be installed from the repository. You will not have to re-install the package again, and to use the package load it with the library() function. For example:
library(tidyverse)
All packages will be installed in your user folder.
To install a specific package version you can specify:
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_version("tidyverse", "1.3.2")
We recommend starting R using Rstudio for best results, instead of double clicking on a R or Rmarkdown script.
Python packages
Similar to R packages, Python packages may be installed using the Package Installer for Python (pip).
We recommend installing python packages from the command line. If you start Jupyter lab, and choose the Terminal tab:

Then install your package using pip, for example, to install the pandas package:
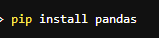
Then you may use the package within your Jupyter notebook as usual.
Note: Please include the option
--userat the end of the pip command.
To install a specific package version type
pip install pandas==1.2.3 --user
